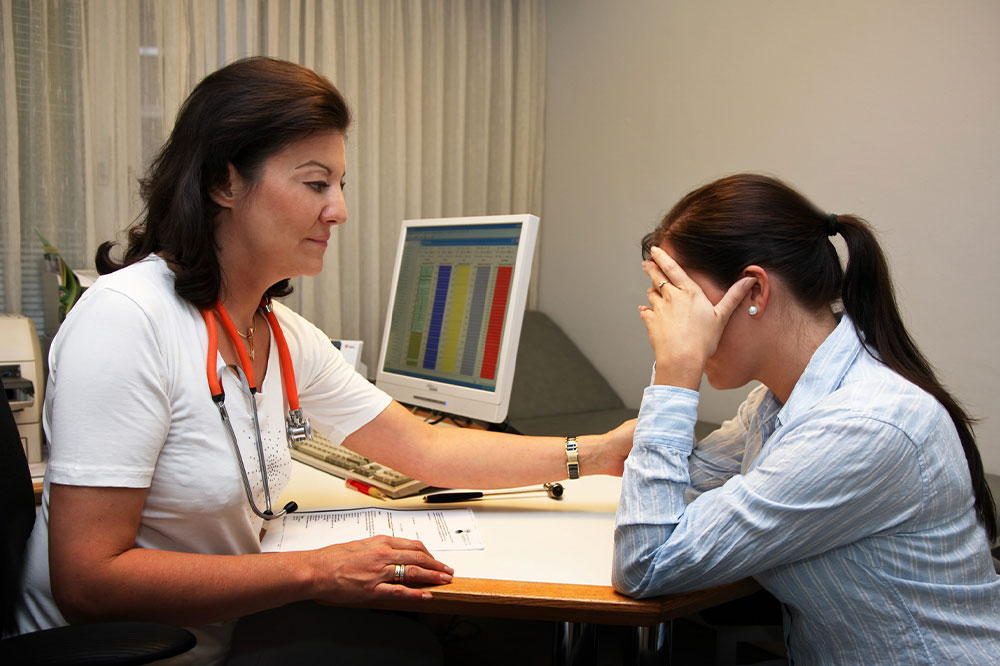
Esophagus is the muscular tube that connects the throat and the stomach. Esophageal cancer is a form of cancer that affects this muscular tube. It is rare cancer that can also lead to life-threatening complications. Most patients are diagnosed with this condition in its advanced stages as this type of cancer does not show symptoms in the initial stage. Keep reading to learn more about some common alarming signs of esophageal cancer.
Warning signs of esophageal cancer
Difficulty swallowing
Also known as dysphagia, facing trouble swallowing is one of the most common signs of esophageal cancer. Dysphagia can occur because of a tumor that makes it difficult for food to pass through by obstructing the esophagus. The pain and difficulty in swallowing may be because of damage to the nerves that control the movement of esophageal muscles. Alternatively, it can also happen because of physical obstruction. As the tumor grows, the patient might experience increasing pain and difficulty swallowing solid food and eventually face problems with liquids. However, this symptom can also be attributed to several other health conditions.
Acid reflux
Acid reflux is considered one of the common indicators of esophageal cancer. It occurs when the contents of the stomach or the hydrochloric acid in the stomach go back up into the esophagus. It can cause irritation and inflammation of the food pipe. Chronic acid reflux can result in Barrett’s esophagus. It is a condition in which the esophageal lining changes, making it more susceptible to developing cancer.
Chest pain
Another symptom of esophageal cancer is chest pain. This results from cancer cells have invaded the chest or the back wall. This chest discomfort can be constant, or it may come and go. Some might even experience worsening pain over time. However, various other conditions share this symptom, so it is important to have yourself examined by a health expert immediately.
Unintentional loss of body mass
Another symptom of esophageal cancer can be body mass loss without trying. This change in body mass is because cancer cells eat up the energy from the body’s reserves. It can also happen when patients find it hard to eat enough food due to the trouble they face while swallowing. It can also indicate the spread of cancer to other body parts. Any significant, rapid change in body mass should be evaluated by a doctor as it is a concerning symptom.
Chronic cough or wheezing
Persistent coughing and wheezing can be symptoms of esophageal cancer. Chronic cough can occur when the tumor presses onto the vocal cords or when cancer cells make their way to the lungs. Chronic cough and wheezing can result from other health concerns, so it is important to consult a doctor to get tested.
Regurgitation of foods or fluids
Esophageal cancer can cause regurgitation of foods and fluids. Regurgitation is when undigested food or liquids travel back to the mouth or the esophagus. It can occur when the tumor physically obstructs the esophagus or when cancerous cells spread to the stomach.
Unexplained vomiting
Vomiting can also be considered a symptom of esophageal cancer. It can occur when cancer cells enter the stomach or the tumor obstructs the esophagus. Unexplained vomiting can also indicate that cancer has metastasized to other body parts.
Chronic indigestion
Chronic indigestion can also be considered a sign of esophageal cancer. It can happen if cancer cells or tumor affects the digestive system’s regular functioning. Some other problems that can arise include nausea, bloating, and discomfort after eating.
Hoarseness
Change in voice or hoarseness can also be considered a sign of esophageal cancer. This change results from a tumor pressing on the person’s vocal cords or when cancer has reached the throat. If someone experiences a change in voice or persistent hoarseness, it is important to get it examined by a doctor immediately to rule out the possibility of cancer.
Fatigue
Fatigue is a symptom shared by various health conditions and types of cancer, including esophageal cancer. It can occur due to the disease or be a side effect of a particular treatment. Fatigue may necessitate lifestyle adjustments on the patient’s part, as it can significantly affect one’s quality of life.
Hiccups
In rare cases, persistent hiccups can occur as a sign of esophageal cancer. When tumors irritate the diaphragm, it causes spasms that result in hiccups. While hiccups are not generally a cause of concern, persistent hiccups must be evaluated by a healthcare professional. Usually, hiccups last a few minutes, but if it doesn’t resolve, they can indicate a severe underlying condition.
Bone pain
Esophageal cancer can metastasize to other body parts, including spreading to the bones. It can give rise to bone pain in the hips, back, and other parts of the body. A patient can experience severe bone pain that can impact their ability to perform day-to-day tasks. If esophageal cancer has made its way to the bones, it may be considered an advanced stage of cancer and may call for aggressive treatment.
Swelling of the abdomen
Fluid buildup and swelling of the abdomen can occur in the advanced stages of esophageal cancer. It occurs when cancer has spread into the abdominal cavity. It can cause bloating, discomfort, difficulty breathing, and a feeling of fullness.
Bloody stools
The disease can also cause bleeding in the digestive tract. It is reflected in the form of blood in the stools. The stools may appear blood red or black and tarry.
Shoulder pain
If esophageal cancer has spread to other organs in the body, it can result in shoulder pain. It happens when the cancer cells press on the nerves running through the shoulder and chest.